Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that we cannot live without. They also play a critical role in fighting cancer, heart disease, and inflammation. They're also found in super delicious foods that you can easily add to your diet every day.

QUICK REFERENCE
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Most of the fats needed by the human body can be made in-house, so to speak. The human body can use other fats or raw materials to manufacture vital fats. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats, meaning that the body cannot make them from scratch and they must be obtained through food sources.
As omega-3 fatty acids have to enter the body through the diet, it is important to include omega-3-rich food sources as part of a healthy diet.
Good dietary sources of omega-3s include:
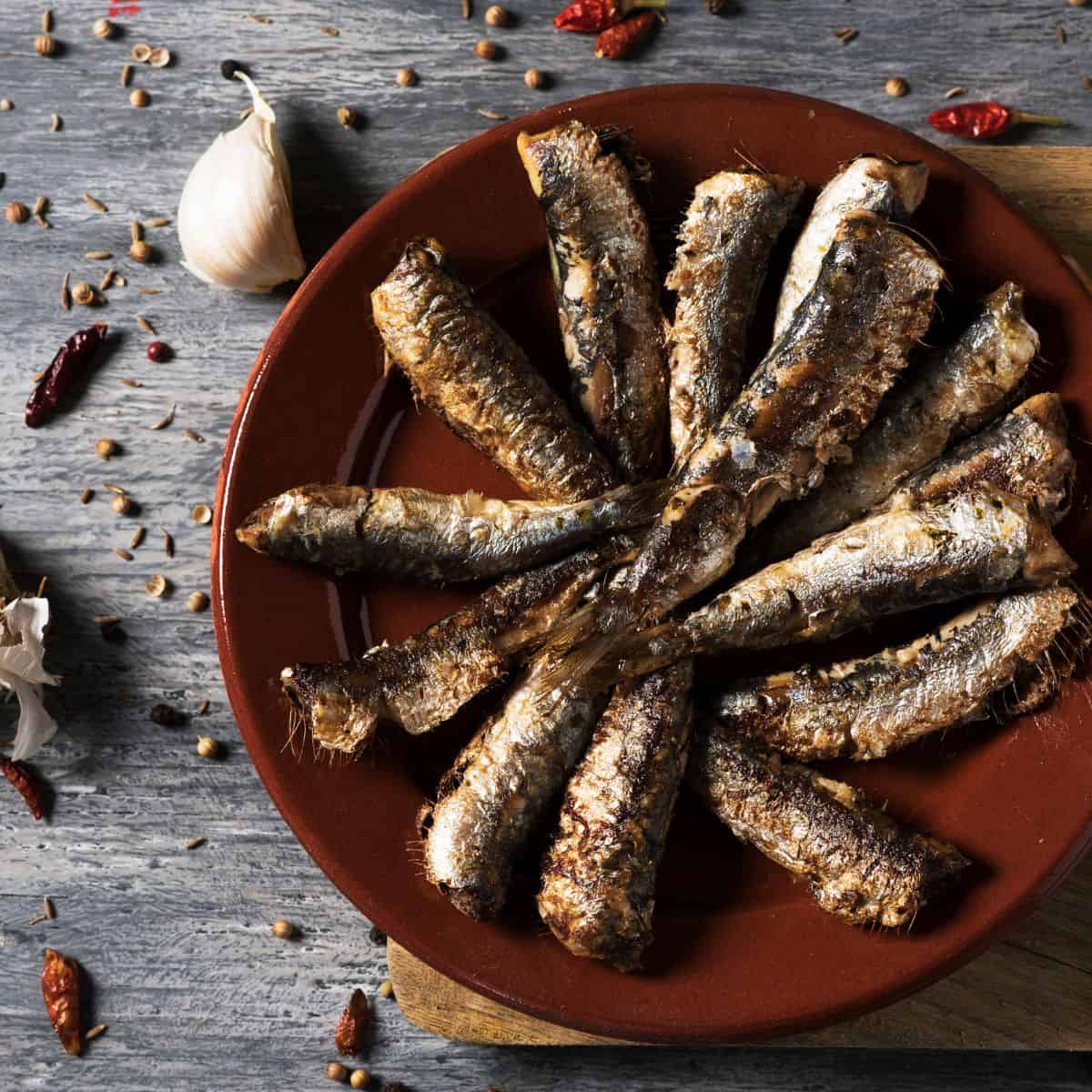
- Fatty fish, like mackerel, salmon, tuna, herring, sardines, and anchovies
- Cod liver oil
- Caviar
- Oysters
- Flax and chia seeds
- Flax seed oil
- Walnuts
- Leafy green vegetables
Three Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are mainly found in fish, seafood, and algae.
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), is the fat that is primarily found in vegetarian sources and is the omega-3 fatty acid that is most common in Western diets.
Omega-3 fats are an integral part of cell membranes throughout the body and affect the function of receptors in the cell membranes. They are essentially the beginning point for making hormones that regulate arterial vessels, blood clotting, and inflammation, which is why they are crucial for both a healthy body and longevity.
Health Benefits
Researchers have been studying the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for quite some time and those benefits have been stacking up! Here are some of the highlights of how omega-3 fatty acids can improve your health and well-being.
Improving Heart and Cardiovascular Health
In 2006, the Cardiac Societies recommended taking 1g/day of both EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD). (1) This recommendation came on the heels of several scientific studies that concluded that omega-3 fatty acids prevented CVD and sudden death from cardiac events and arrhythmias. Other studies showed a significant reduction in triglyceride and cholesterol levels, and that omega-3s helped lower blood pressure. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce the risk of ischemic stroke in both men and women. (2)
Cancer Prevention
Epidemiological studies involving a large population of Norwegian women showed that women who consumed high amounts of fish known to be high in omega-3 fatty acids were 30% less likely to develop breast cancer, and women with cancer had a 30% reduction in mortality. Other studies demonstrated that there was a significant reduction in both endometrial and ovarian cancer, and a study of men found that those who supplemented with omega-3-rich fish oil had a decreased risk for prostate cancer when compared to men who ate fish twice per week. (2)
Reducing Inflammation
Possibly one of the most important health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids is their role in moderating the inflammatory responses in the body. Even though inflammation is a necessary and vital function of the body, many diseases are caused by excessive or inappropriate production of inflammatory mediators, and it has been shown that EPA and DHA act in many ways to reduce inflammation, including reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and proteins and increasing the production of anti-inflammatory eicosanoids and inflammation resolving resolvins. (3)
Because of the anti-inflammatory effects within the body, supplementation with or eating a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids has been shown to offer some benefits to disease conditions where inflammation plays a key role, including:
- Autoimmune conditions
- Diabetes
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Asthma
- COPD
- Psoriasis
- Atherosclerosis
- Acute cardiovascular events
- Neurodegenerative conditions (3)
The Importance of Omega 3:6 Ratios
It has been suggested that humans evolved to eat a diet that was balanced in both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. In today’s standard American diet or a typical Western diet, instead of a ratio of 1:1, that ratio is between 15:1 and 16.7:1, showing an excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids and a deficiency in omega-3s. (4) An evolutionary diet is the diet on which human genetic patterns were established and deviating from that pattern could very well be the source of increasing numbers of people suffering from autoimmunity, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other inflammatory conditions.
Several scientific studies have shown that increasing levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet and bringing that ratio of omega-3s to omega-6s much lower exerts strong suppressive effects on inflammation and has an overall beneficial effect concerning the disease process. As scientists are realizing the importance of this ratio on overall health, they are finding that different ratios benefit different diseases. For instance, a study on colorectal cancer patients showed that a 2.5:1 ratio reduced rectal cell proliferation, but a 4:1 ratio had little to no discernible effect. (4) But overall, even if a particular ratio is better for one disease over another, a lowering of the ratio plays a positive role in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms and outcomes.
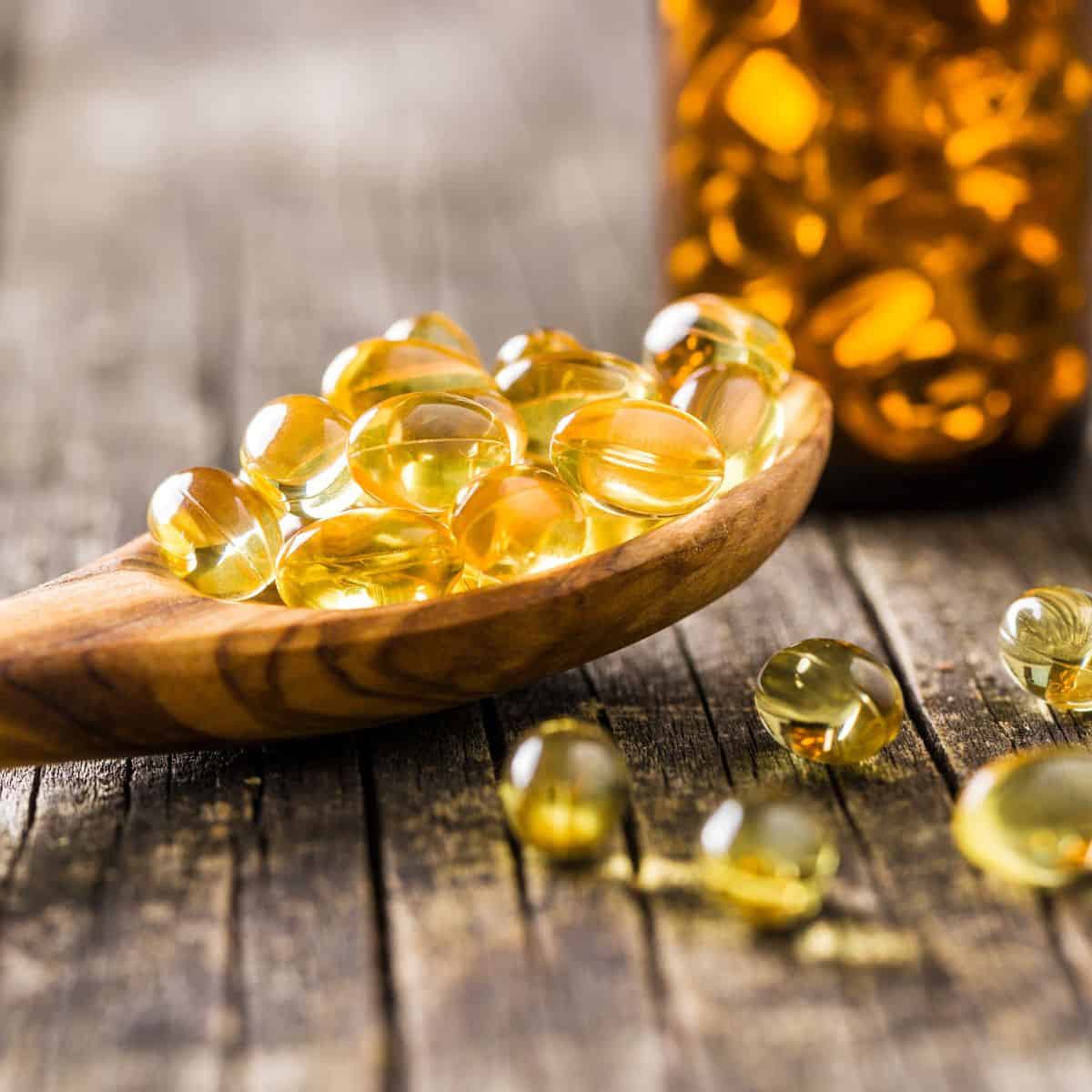

Increase Your Intake
Though it is well known that there are many health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, research has not yet reached a consensus on just how much EPA and DHA is the optimal dose per day. Recommended daily amounts haven’t been established and most dieticians and health experts suggest daily intakes based on a number of considerations, including the person’s stage of life, current health conditions, nutritional intake, and what the most current research supports. Because it is established that omega-3 fatty acids are crucial in the fight against inflammation and they are part of the foundation for cellular health, they would be considered a vital component to optimize both health and longevity.
The best place to start is by increasing omega-3-rich foods in your diet or supplementing with fish or flax seed oil. Just remember, it’s also important to consider the source of fish or fish oil supplements and whether or not it’s sustainable. Sustainable fishing is crucial for the health of the oceans and natural habitats. Sustainable practices also help to reduce pollution and bycatch, while providing the highest quality supplements or whole food products. With such promising health benefits, it’s worth finding a high-quality source of omega-3 fatty acids to keep you healthy and thriving.
Omega-3 FAQs
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to aid in cancer and heart disease prevention and reduction of inflammation.
The most bio-available (useable) sources of omega-3 fatty acids are animal sources including fatty fish, cod liver oil..
Omega-3s can be found in flax and chia seeds, walnuts, and leafy greens.
Sources
- von Schacky C, Harris WS. Cardiovascular benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73(2):310-315. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.08.019
- Patrick R. The Importance of Omega-3. [Internet ebook] [cited 22nd July 2019] Available from: https://www.foundmyfitness.com/ebook/importanceofomega3.pdf.
- Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients. 2010;2(3):355-374. doi:10.3390/nu2030355
- Simopoulos AP. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002;56(8):365-379. doi:10.1016/s0753-3322(02)00253-6


















Comments
No Comments